Introduction
If you’ve been keeping up with this series (sorry for the hiatus - I had school work and camps) you know that AI is rapidly changing our world, from how we shop to how we receive learn. But as AI becomes more integrated into our daily lives, it raises important questions: Who controls these powerful technologies? How do we ensure they’re used responsibly? And what happens when something goes wrong? These questions are the literal heart of AI regulation, a topic that governments around the world are grappling with. In this post, we’ll take a look at how different countries are approaching the regulation of AI, and what this means for the future.
Why Do We Need AI Regulation?
Before diving into the specifics, let’s talk about why AI regulation is important. AI can do amazing things and is revolutionizing numerous industries, but it also has the potential to cause harm. For example, AI systems can be biased, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups of people. They can also be opaque, meaning it’s hard to understand how they make decisions. Without proper regulation, these issues could lead to serious consequences, such as discrimination or privacy violations. We’ve already covered such possibilities in previous blogs, so we won’t go into a lot of detail about that here.
Regulation is needed to set clear rules and standards for the development and use of AI. This ensures that AI is used in ways that benefit society while minimizing potential risks.
The EU:
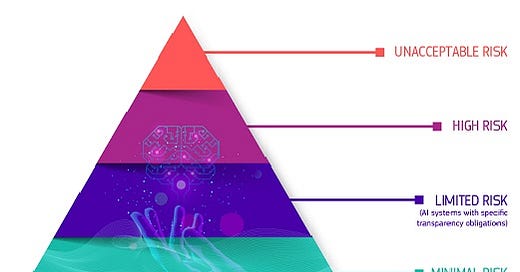
The European Union (EU) has been one of the most proactive regions in developing AI regulations in recent years. In 2021, the European Commission proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act, which aims to create a legal framework for AI across the EU. The Act classifies AI systems into different risk categories, ranging from minimal risk (like spam filters) to high risk (like AI used in critical infrastructure).
High-risk AI systems are subject to stricter regulations, including transparency requirements and regular assessments.
The EU’s approach is primarily focused on protecting fundamental rights, such as privacy and non-discrimination.
The United States: A More Flexible Approach
In contrast to the EU’s strict regulatory framework, the United States has taken a more flexible approach to AI regulation. Instead of creating a single, overarching law, the U.S. has opted for sector-specific guidelines and voluntary standards. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed a framework for AI risk management, which organizations can use to guide their AI development processes.
The U.S. approach is designed to reinforce capitalism; it emphasizes innovation and competitiveness. The idea is to avoid stifling technological progress while still addressing the numerous ethical and safety concerns.
Unfortunately, it is a little long to summarize in this short article. I may consider releasing a summary in its own separate article. For now here are some resources if you want to learn more:
https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ai/NIST.AI.600-1.pdf
China: Government-Controlled AI Development
China’s approach to AI regulation is heavily influenced by its government’s centralized control. The Chinese government has made AI a top priority in its national development strategy, with the goal of becoming the world leader in AI by 2030. (Source) To achieve this, China has implemented a combination of strict regulations and state-driven initiatives.
China’s AI regulations focus on ensuring that AI aligns with government priorities, such as national security and social stability. This includes strict oversight of AI systems, especially those used in surveillance and data collection. While this approach has enabled rapid advancements in AI, it has also raised concerns about privacy and human rights.
Comparing Global Approaches
When we compare these three approaches, it’s clear that there is no “one-size-fits-all” solution to AI regulation. The EU’s focus on human rights, the U.S.’s emphasis on innovation, and China’s government-led, more restrictive, strategy each reflect different priorities and cultural values.
The EU’s model is often praised for its strong ethical standards, but it may slow down innovation due to its stringent rules. The U.S. model, on the other hand, promotes rapid technological advancement but may not provide enough protection against the risks associated with AI. China’s model shows how AI can be rapidly developed under a centralized strategy, but it also highlights the potential dangers of state control over technology.
What’s Next?
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the regulatory frameworks that govern it. We can and should expect to see more international cooperation on AI standards, as well as increased efforts to balance innovation with ethical considerations. Future regulations will likely need to be adaptable, as AI technology is constantly changing and presenting new challenges.
For individuals and businesses, staying informed about AI regulations is crucial. Understanding the different approaches to regulation can help you navigate the complex landscape of AI, whether you’re developing AI technologies or simply using them in your daily life.
Conclusion
AI regulation is a complex and rapidly evolving field. Different countries are taking different approaches, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. By understanding these global perspectives, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities that come with regulating such a powerful technology. As AI continues to shape our world, it’s important to stay informed and engaged in the conversation about how it should be governed.